Cryptocurrencies or “digital money” — not just the implementation of a mathematical theory of absolute encryption or a means of payment, but also a trendy trend among those wishing to earn quick income where few understand where the money comes from.
In this article, we will explain what blockchain is — the foundation of the crypto world, without which there would be no exchange-traded crypto futures, crypto exchanges, or BTC/USD quotes in trading terminals.
Before discussing the basics of blockchain, it is worth mentioning the most common stereotype — that this technology is used exclusively in cryptocurrencies. This myth has been created by the media and the Internet, but in reality, this is far from true: the principles of decentralized storage are applicable everywhere where high confidentiality and protection from unauthorized access are needed, for example, in hospitals.
Reasons for Emergence
Intermediaries are present in any sphere of human activity, especially many in legislative and financial processes: banks guarantee the correctness of monetary transactions, notaries and government agencies confirm originals and copies of various documents, fiscal authorities monitor to ensure nothing is hidden from taxes.
Of course, intermediaries are necessary, but as centuries of practice have shown, they cannot (or do not want to!) ensure 100% reliability and trust. We all know cases of document forgeries, registry data, and bank account falsifications. To minimize human factor influence, blockchain technology was created, which has no mechanism for intermediaries, and now (we hope!) it is possible to be confident in the immutability of stored data.
Since there is no central payment center, a new “trust scheme” was needed between the sender and receiver, which in the crypto world operates on the principle of mutual guarantee (routine escrow mechanisms): payment confirmation is made by network nodes based on unique blocks and keys.
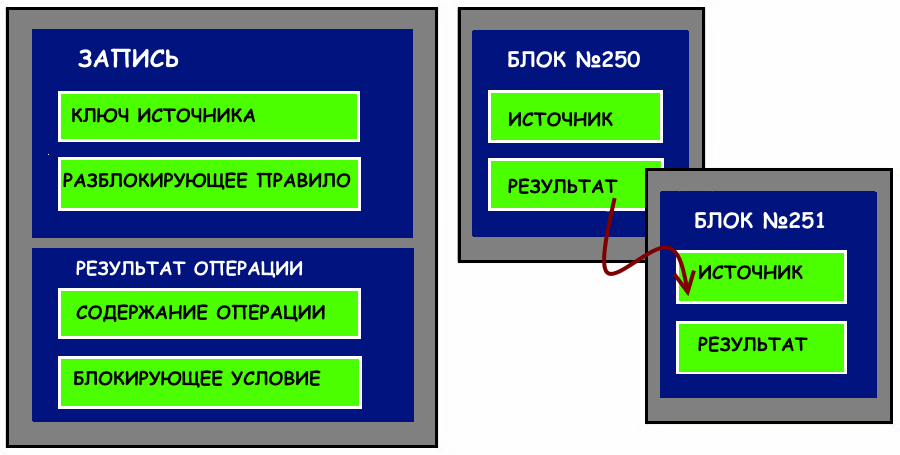
Cryptographic Keys
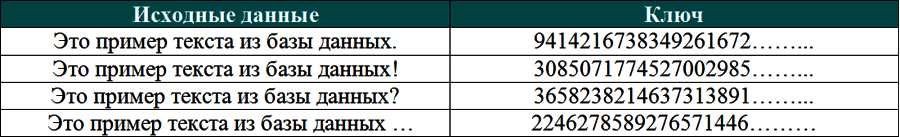
This is the basis of the new network: with their help, the authenticity of information added or stored in the database can be verified in real-time. From a mathematical point of view, for beginners, they are large numbers calculated using a hash function algorithm.
For each set of data, there is a unique hash function with the following features:
- Even with a key, it is impossible to obtain the original data — this is how full confidentiality is maintained;
- Any change in data results in a new key (hash).
Thus, having only the unique key, we can already use it to confirm various operations with the blockchain (and not only financial ones!). Verifying authenticity is very simple — just take the original data and recalculate the hash function.
How the Blockchain Network Works
Each node has full rights and contains (in the initial version) the complete transaction history from the moment the network was recorded. In the case of cryptocurrencies, the current database takes up a huge amount on the hard drive and constantly increases. For payment processing, information from the last 3-4 months is sufficient, but let’s assume that the node (wallet) stores a full copy.
Nodes (for Bitcoin, at least 6 are required), confirming the authenticity of a new operation, are selected randomly, after which they are transmitted into blocks with their own unique hash keys, which miners search for. If the crypto-transaction is legitimate, its data is recorded in the general database, which is synchronized among all nodes, and then the information cannot be changed.
From the perspective of blockchain principles, a transaction (operation) is considered genuine only after it has been added to a block, and this verification process takes time. Yes, payments with incomplete confirmation can be used, but in this case, the network cannot guarantee the absence of distortions or data substitutions.
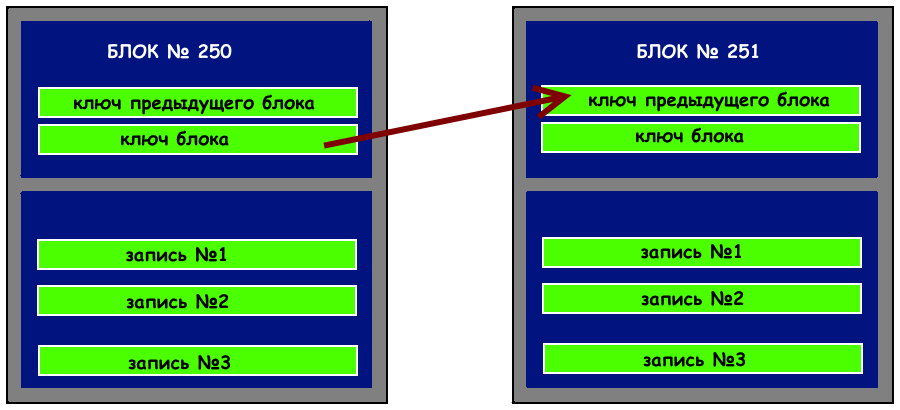
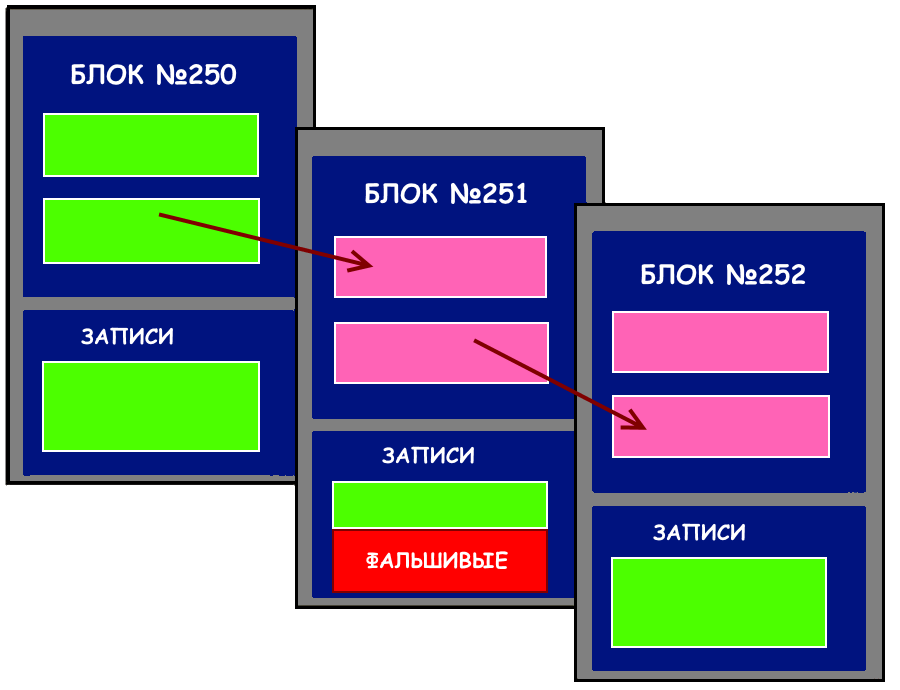
What a Block Consists Of
Now, more details about the structure of a “block” or, as mentioned above, a set of individual records — money transfers, changes to registry data, buying/selling goods, etc. The main elements of a block are the header and the previous hash key. It is with its help that protection from hacking and forgery is ensured.
Each new block must contain the hash of the previous one, and to change its data, access to all its “ancestors” in the blockchain is required. The more operations, the longer the “chain of keys,” but they can be viewed in open access, and any network user can verify the absence of gaps, repetitions, and other discrepancies.
In simple terms, blockchain technology can be likened to a set of DNA molecules — each contains the full set of genetic data. Like living organisms, any change (mutation or deliberate addition of new elements) requires increasing effort, as each change proportionally increases the network’s (organism’s) complexity.
And maybe, hacking is still possible?
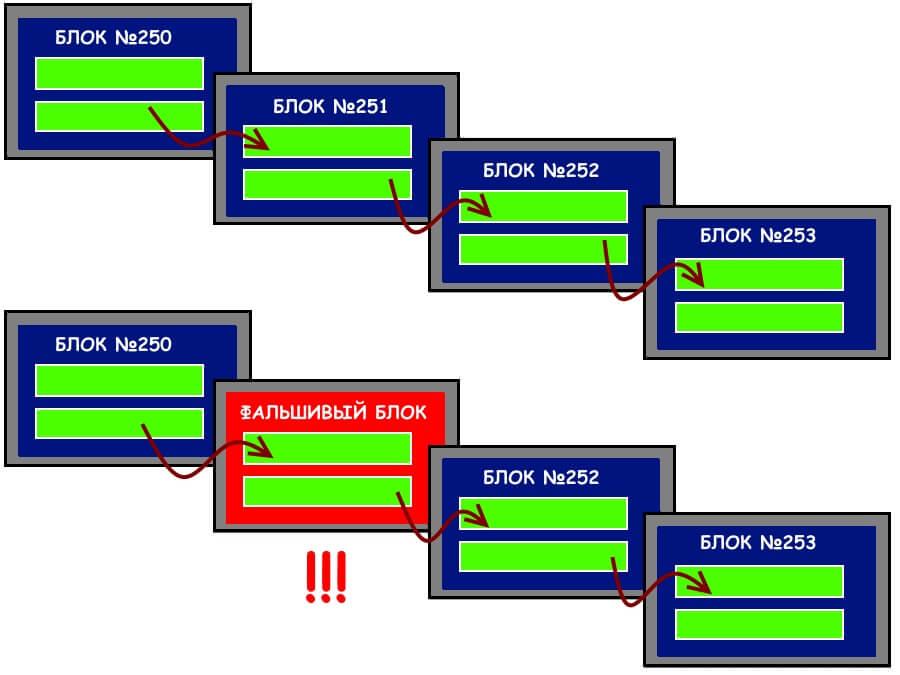
Theory is good, but let’s see how the network works when attempting to forge block chains and the data they contain. Is everything really as reliable as supporters of crypto technology claim? Let’s try changing a block:
Even at first glance, the forgery is clearly visible — in block №253, there will be no “our” key, and further confirmation will be immediately stopped. The reader might object: you could change the entire previous chain, and the deception wouldn’t be detected. Yes, in theory, this is possible, but here, the scale of the network begins to act as a guarantee. The more active it is, the longer the chain of blocks, especially when it comes to cryptocurrencies. New data is constantly added, and the attacker physically cannot replace all the blocks.
The problem of substituting all or most blocks does not have a solution in cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, where the algorithm does not provide for the emission of all coins at once, and they must be gradually added to circulation through mining. For this, one or more pools need to control more than half of the network’s power — this scheme is known as “51% attack”. It becomes possible to issue blocks without full confirmation, and to prevent such situations, strict restrictions are imposed on these currencies.
Editing the Database
It’s good if we are not able to forge all blocks in a reasonable time, so let’s take another approach and make changes to the already existing one, usually the last. And again, Blockchain prevents this through the same keys:
As soon as the block data changes, the process of recalculating the current hash begins. And since the following blocks store the correct data, the system will immediately detect the forgery. For added security, the following may also be used:
- Linking records into additional chains with a reference table to all previous ones (sources);
- Rules defined by both parties to the deal, under which it is considered correct, for which a smart contract is used, like in E
In conclusion. Today, the question “what is blockchain?” no longer seems strange — this mechanism has already become an integral part of the new digital world. The EU Parliament has already conducted a trial vote using blockchain and is considering a similar project for organizing elections in government bodies. Stock and banking operations, legal and legislative activities, even copyright enforcement — all increasingly involve successful use of crypto technologies, so we will have to learn how to use all this.